Module 1: Water and Plant Cells
-
Module 1: Water and Plant Cells
-

-
-
-
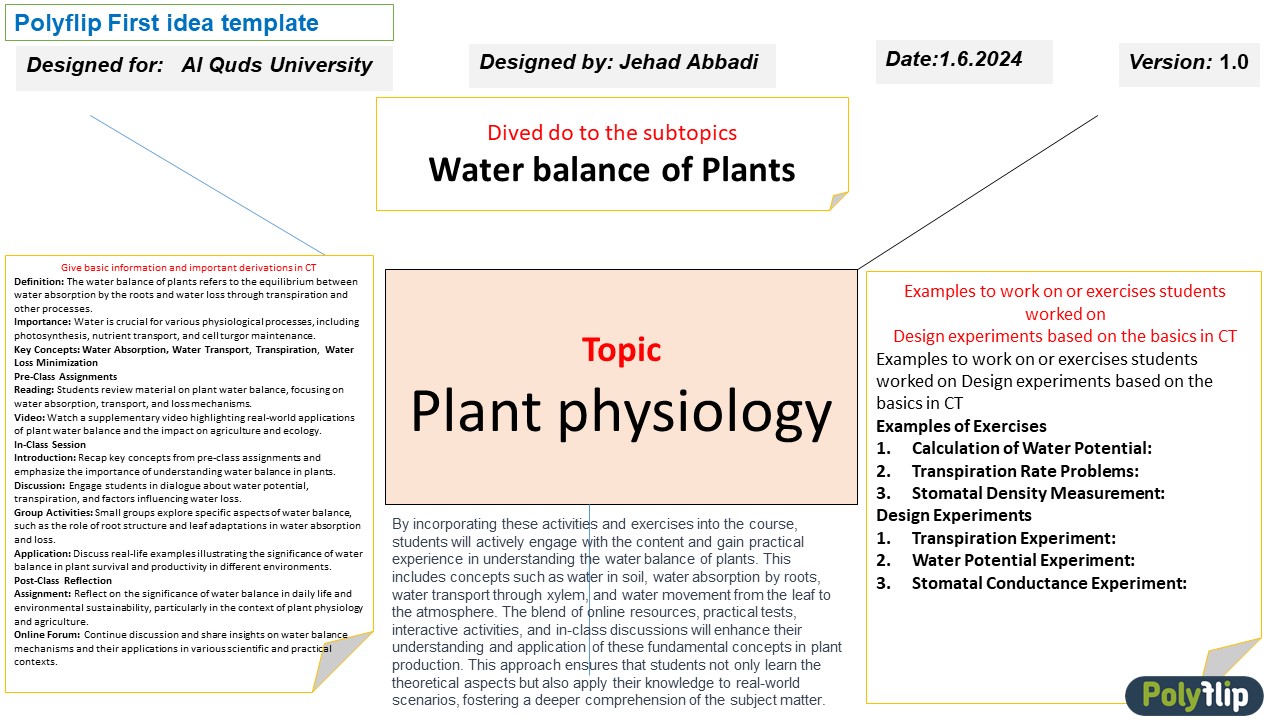
Module Description
In this module, students will explore the vital role of water in plant physiology, focusing on its interactions with plant cells. Adopting a flipped classroom approach, students will first engage with foundational concepts through pre-class materials, including videos, readings, and quizzes. These resources will introduce essential topics such as the structure and properties of water molecules, water transport mechanisms, and the principles of water potential.
During in-class sessions, students will actively apply their pre-class learning through collaborative activities, problem-solving exercises, and hands-on experiments. Key concepts such as osmosis, transpiration, and water potential will be explored in-depth, with a focus on understanding how environmental factors influence water movement within plants.
Students will conduct experiments to measure water potential and osmotic potential in plant cells, critically assess the role of different plant structures in water uptake, and analyze experimental data to draw meaningful conclusions. Emphasis will be placed on collaborative work, effective communication of scientific findings, and the development of problem-solving skills.
By the end of this module, students will have a comprehensive understanding of water's significance in plant life and be equipped with the skills to conduct and analyze experiments related to plant water relations. This flipped classroom model encourages active learning, critical thinking, and the practical application of theoretical knowledge.
-
Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs)
ILO1: Explain the significance of water in plant life, focusing on its role in physiological processes such as photosynthesis, nutrient transport, and cell turgor maintenance.
ILO2: Describe the structure and properties of water molecules, including polarity, cohesion, adhesion, surface tension, specific heat, and heat of vaporization.
ILO3: Define key concepts of water transport in plants, including osmosis, transpiration, capillary action, and root pressure.
ILO4: Understand the principles of water potential and its components, and how it influences water movement in plants.
ILO5: Analyze the impact of environmental factors on the rate of transpiration and water transport in plants.
ILO6: Evaluate experimental data to determine water potential and osmotic potential in plant tissues.
ILO7: Assess the role of plant structures (roots, stems, leaves) in facilitating water uptake and transport.
ILO8: Conduct experiments to measure osmosis in plant cells and apply techniques for calculating water potential using experimental data.
ILO9: Collaborate effectively in group settings to design, execute, and analyze experiments related to plant water interactions.
ILO10: Communicate scientific findings clearly through written lab reports, presentations, and discussions, and reflect on personal learning to identify areas for improvement.
-
