PTUK Course (1): Solar Energy Systems (renewable energy)
Calculations related to batteries’ connections.
Battery Efficiency:
Battery efficiency (ηAh): is the ratio of the energy taken from the battery (number of Ah discharged), to the energy provided to the battery to be fully charged (Number of Ah required to fully charged it).
Battery efficiency ηWh
Depth of Discharge (DOD): is defined as the capacity that is discharged from a fully charged battery, divided by battery nominal capacity. Depth of discharge is normally expressed as a percentage. (Manufacturer specification)
State of Charge (SOC) = 100%- DOD
Battery System Connection: (Series /Parallel)
This depends on: Total Ah capacity; DC bus voltage; The CAh of each battery; and the voltage of each battery.
CAh-total = CWh-total / DC bus voltage.
- Number of series batteries in each string = DC bus voltage / voltage of each battery
- Number of parallel strings = CAh-total / CAh-each battery.
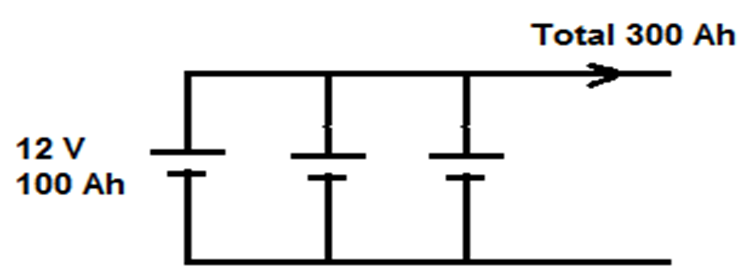
Example1: A total storage of 3600 Wh is required by a battery system where the DC bus voltage is 12 V. Build the battery system that uses 12 V battery with 100 Ah each.
Number of series batteries in each string = DC bus voltage / voltage of each battery = 12/12 = 1
CAh-total = CWh-total / DC bus voltage = 3600 / 12 = 300 Ah.
Number of parallel strings = CAh-total / CAh-each battery = 300 / 100 = 3 Strings
Battery System Connection: (Series /Parallel)
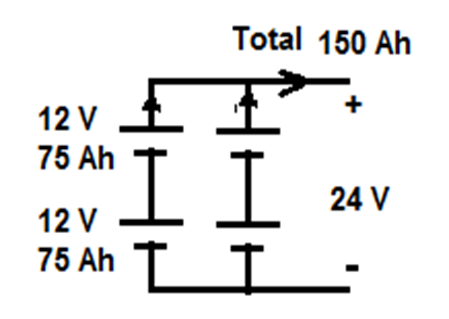
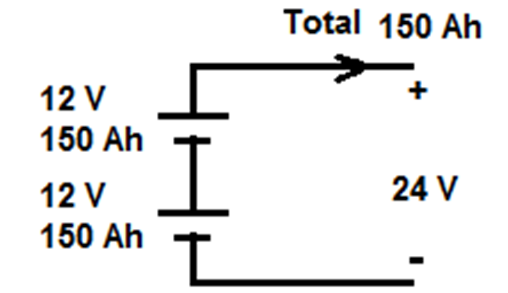
Example 2: A total storage of 3600 Wh is required by a battery system where the DC bus voltage is 24 V. Build the battery system that uses 12 V battery with 150 Ah each.
Number of series batteries in each string = DC bus voltage / voltage of each battery = 24/12 = 2
CAh-total = CWh-total / DC bus voltage = 3600 / 24 = 150 Ah.
Number of parallel strings = CAh-total / CAh-each battery = 150 / 150 = 1 Strings
Example 3: The same as example 2 but using batteries 12 V and 75 Ah each.